It seems that nowadays all leading companies of different industries are rushing into the metaverse: McKinsey examines if real companies can create value in the metaverse, Bosch opens a Metaverse Lab in Berlin, and Facebook even rebrands to Meta. However, a new buzzword turns out to be a well-forgotten old. Yet in 1992 the term was coined by Neal Stephenson in his science fiction novel titled «Snow Crash». The book depicts a three-dimensional virtual space that exists parallel to the real world, where people interact with each other and the environment as digital avatars and software agents. The new term was eagerly picked up by online video game producers. They created a collection of interconnected virtual worlds that allowed users to travel within and between them, to communicate with other players, and to contribute to the metaverse games with user-generated content.
Since then, the term has been gone far beyond its initial field of origin in science fiction and online gaming and currently is walking in victory in a wide variety of fields – interactive learning, e-commerce, healthcare, real estate, and machine industry. Building on the ideas of virtual, augmented, and mixed realities the metaverse takes it a step further and promises not only to seamlessly connect digital and physical worlds, but also blend different digital platforms and bring together an unlimited number of users and objects. Often addressed as “the metaverse” it has to become a successor of “the internet” – a new space for our virtual existence. Etymologically the Greek word μετά, meaning “after” or “beyond”, emphasizes a transition of the universe, as the ending of the term implies, to a new advanced stage.
A quick internet search results in dozens of definitions of metaverse. It would be quite challenging to give one comprehensive definition for the term as the range of its applications stretches from a digital playground for friends to a commercial space for companies and customers. But what is more crucial than looking for a uniform interpretation is understanding its features and characteristics and exploring new opportunities for industry that are hidden behind.
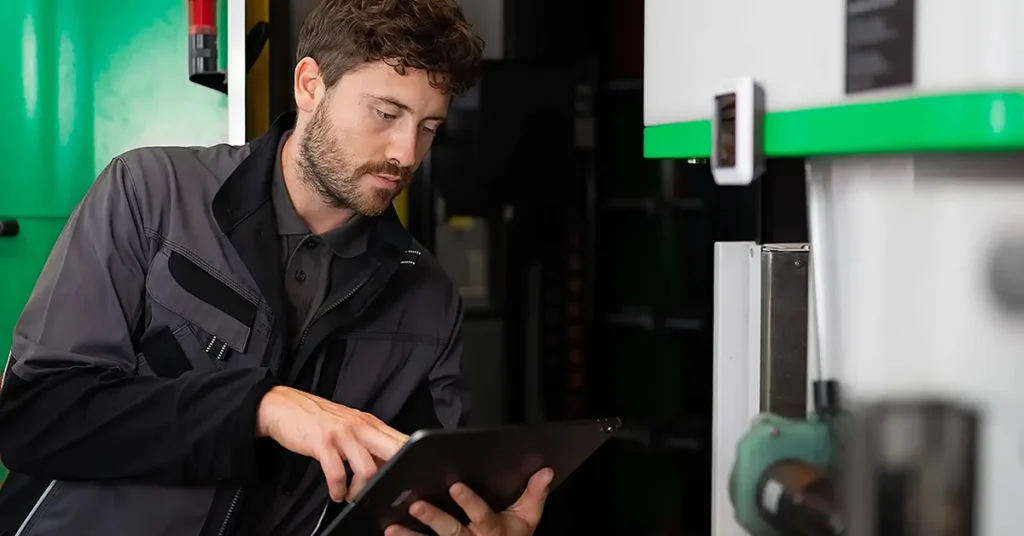
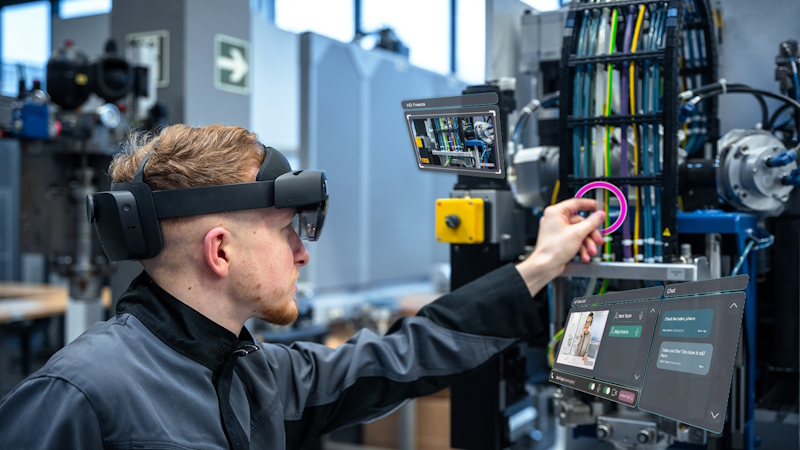
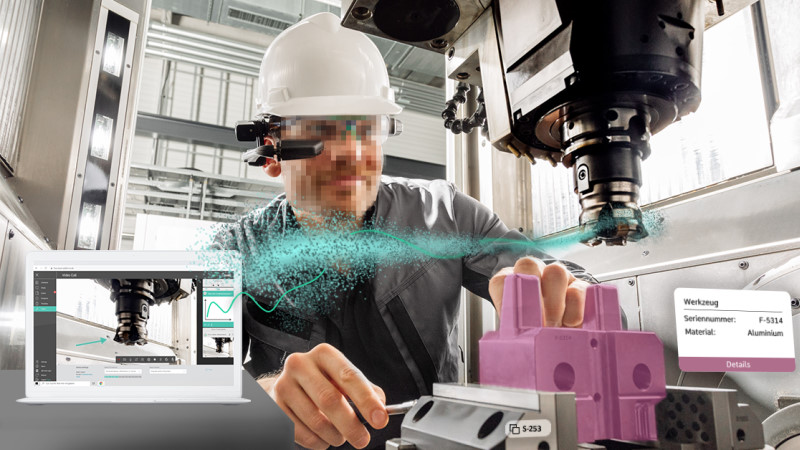
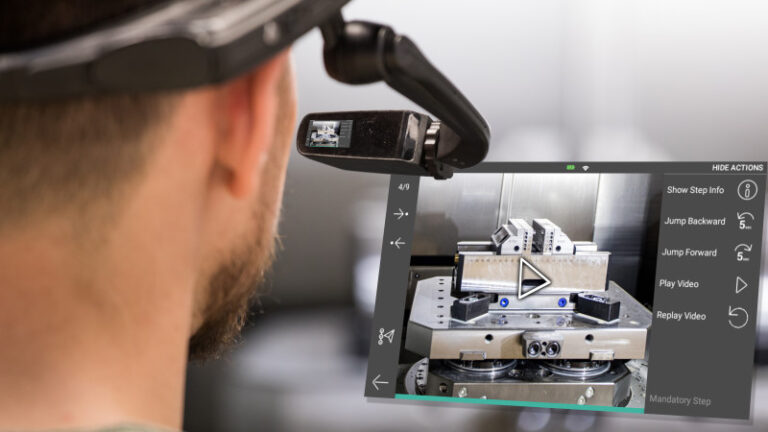
The first important characteristic of metaverse is immersion, which offers an interactive experience spanning across the digital and physical worlds and blending them together. Normally users need to use high technological wearables such as smart glasses or haptic gloves to achieve high levels of interaction and immersive experience. But modern technology makes it possible to interact with digital twins of machines or get instant support while using complex equipment by just pulling a smartphone out of the pocket. A wide distribution of personal electronic devices has made the digital world of metaverse easily available in private as well as industrial settings without the need for extra investment in pricy wearables.
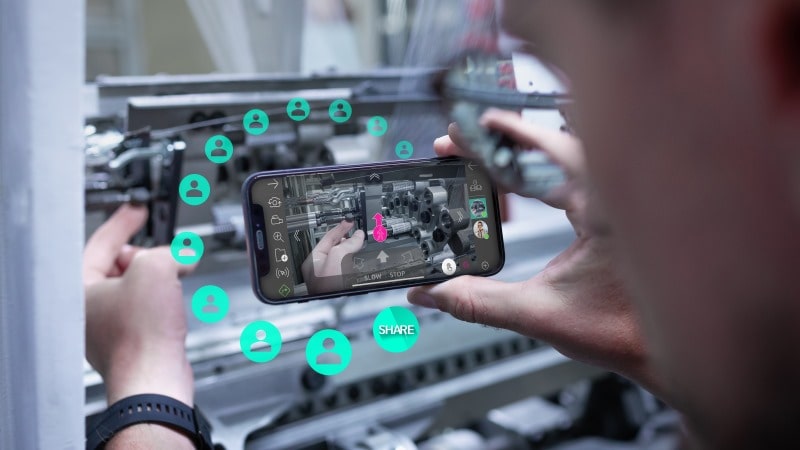
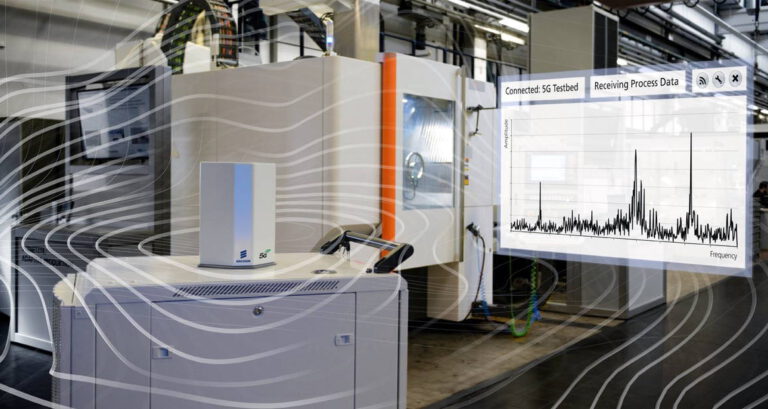
Connectivity is another essential feature holding many applications in industrial environments. The stress is being made not only on connecting an unlimited number of users who can enter the metaverse and interact simultaneously, but also the role and the nature of the users. The roles of users depend on their professional activity – operators, manufacturers, suppliers, dealers, and other stakeholders. Whereas the nature of the users distinguishes between real people and artificial actors, like AI-generated avatars, who guide and support real workers. Moreover, the net of connected users can be expanded and include the entire installed base of a machinery manufacturer or the equipment of a producing industrial company. Each connected asset is mirrored as a digital twin in a system, the generated data is captured for further analysis and optimization of the equipment performance.
The metaverse is characterized by dynamic content because its users have the possibility not only to interact with already existing content but also to create new and make it available to others. The possibility to directly influence the digital environment in collaboration with peers not only positively influences the quality of the content by also helps to form a sense of belonging among the users and form a functional industrial community out of dispersed individuals.
Metaverse brings together different platforms ensuring its constant accessibility and interoperability of available data. As nowadays every company uses at least several if not numerous digital solutions in its processes the challenge is to blend them together into one environment. Application programming interfaces (API) based integration of IT systems and business processes makes that possible. It allows sharing available data among different applications seamlessly interlacing them together into a custom industrial metaverse.
These crucial features help shaping the understanding of the industrial metaverse. The industrial metaverse is a hybrid collaborative space that facilitates the real-world environment with contextualized virtual data and digital platforms that are constantly available for all stakeholders of industrial processes for remote collaboration and self-services.
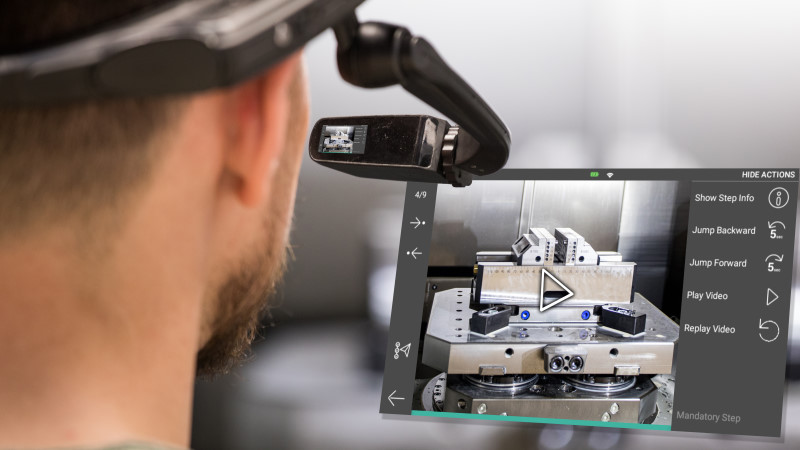
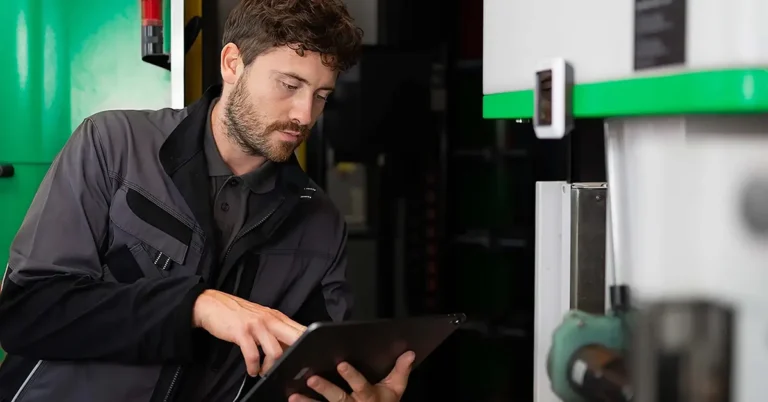
Though the whole idea of the metaverse may still seem quite futuristic to reach it to its full extent, it is already possible to benefit from the advantages it has to offer. The first step any manufacturer could take to pave the way into the new grounds of the industrial metaverse is to augment the physical equipment in use with digital content. Machinery manufacturers as well as companies who deploy equipment in production can take their production processes to an entirely different level through the implementation of smart service and connected worker solutions. These solutions make all relevant technical information from installation to training of the personnel available upon request in step-by-step instructions on a tablet, smartphone, or smart and mixed reality glasses. The necessary information is accessible at the right time and in the right place which ensures flawless production, maintenance, and service processes.
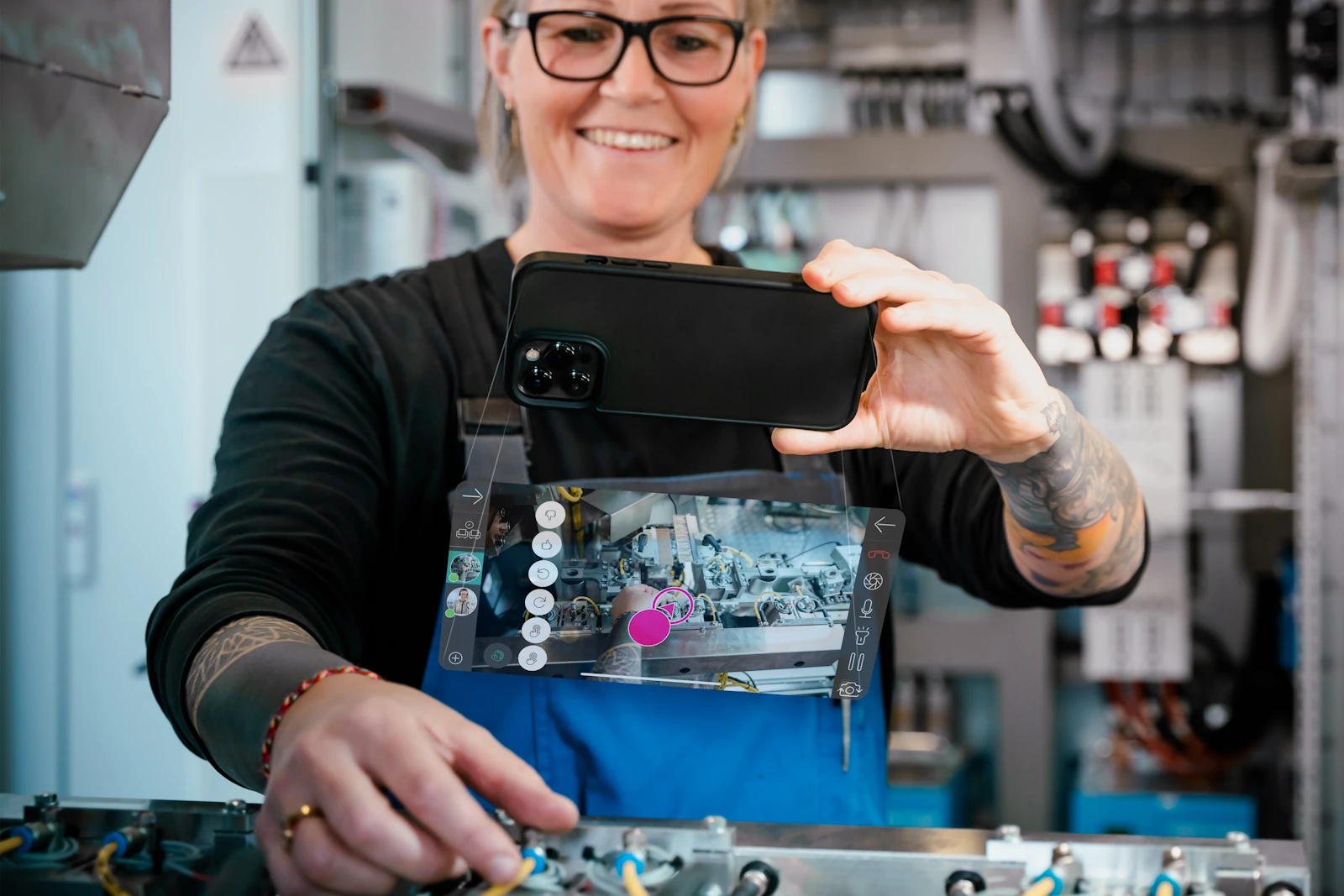
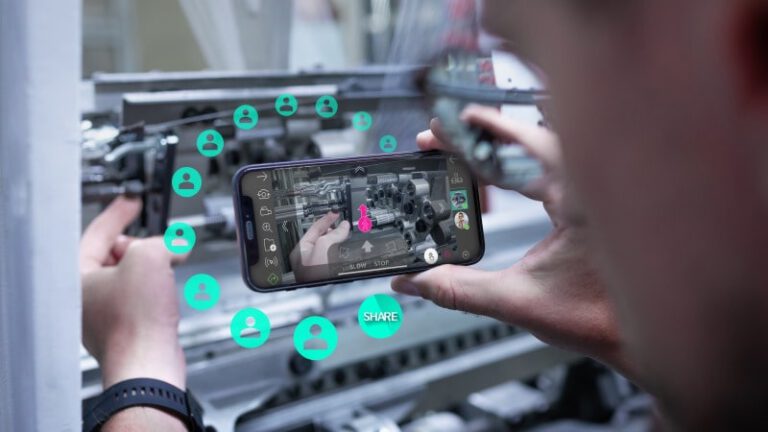
The connective nature of the industrial metaverse can also be experienced by the smart service solutions available on the market. The solutions bring together multiple users who regardless of the numbers can have direct access to the technical information offered by machinery and equipment manufacturers. Moreover, in case of malfunctions of machines and systems that can’t be eliminated by using step-by-step instructions, smart service solutions offer real-time visual assistance from experts. Timely support can help to avoid high costs from prolonged equipment downtime. On the other hand, machinery manufacturers can use smart service platforms to provide users of the installed base with the latest training materials or even create new revenue flows expanding existing business models with digital services.
Users of smart service platforms on their part can take an active role and contribute to the existing content with their feedback or creating new workflows, service tickets, incident reports, or suggesting improvement ideas on machine operation and maintenance. Mutual collaboration of multiple users on certain cases or workflows can help in eliminating repetitive tasks, gaining expertise from different perspectives, and linking numerous stakeholders into one functional industrial community.
Bringing together various modules and making them work as one unit is an important feature of the industrial metaverse . In smart service platforms, it’s being achieved through API-powered integration, which ensures seamless connection with already existing IT systems and lets them exchange data. New data has to be entered only in one application and is then automatically synchronized across other systems. Automated workflows help avoid unnecessary manual input and enable consistent and efficient processes across multiple systems.
oculavis presented its smart service solution at Bosch Metaverse Lab opening and hackathon in Berlin. Bosch welcomed metaverse enthusiasts of all backgrounds to get a sense of the Metaverse Lab and discuss their visions of innovative virtual environments. oculavis was proud to offer the event attendees a chance to participate in a metaverse training scenario. The visitors could directly try a smart service platform out and experience how it can make them familiar with any complex technology. oculavis’ device agnostic approach makes it possible to step into the industrial metaverse by grabbing any available device. Either fancy smart glasses or an ordinary smartphone – both give an experience of how sophisticated machines can be instantly supplemented with digital technical documentation, expert support, or assistance of a multilingual round-the-clock available avatar.
Even though the industrial metaverse is just emerging, its potential to impact production processes, service portfolios, and entire business models is significant. McKinsey reports that just in the first five months of 2022 metaverse start-ups and scale-ups received more than $120 billion of investment, more than double the $57 billion invested in all of 2021. The Gartner 2022 hype cycle for emerging technologies positions the metaverse in the first innovation trigger phase indicating that it belongs to the technologies that will significantly affect business and society in the future.
It suggests that now is the right time for organizations to start to assess the potential of the industrial metaverse and think about how it can be integrated into their existing business models.
Would you like to keep regular track of the latest developments and discover how you can guide your organization into the industrial metaverse? Then use the contact options on this page to get in touch with us!